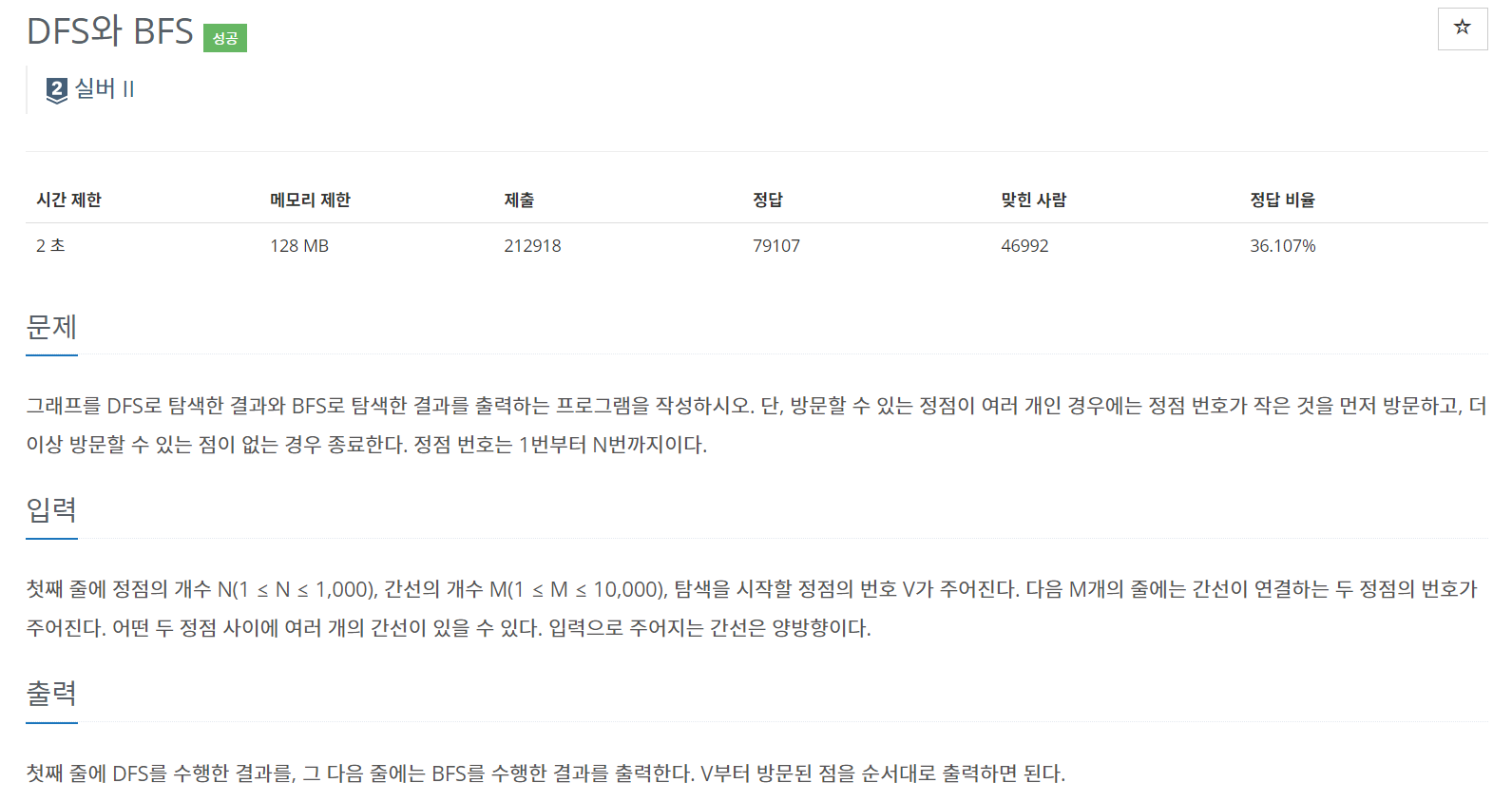
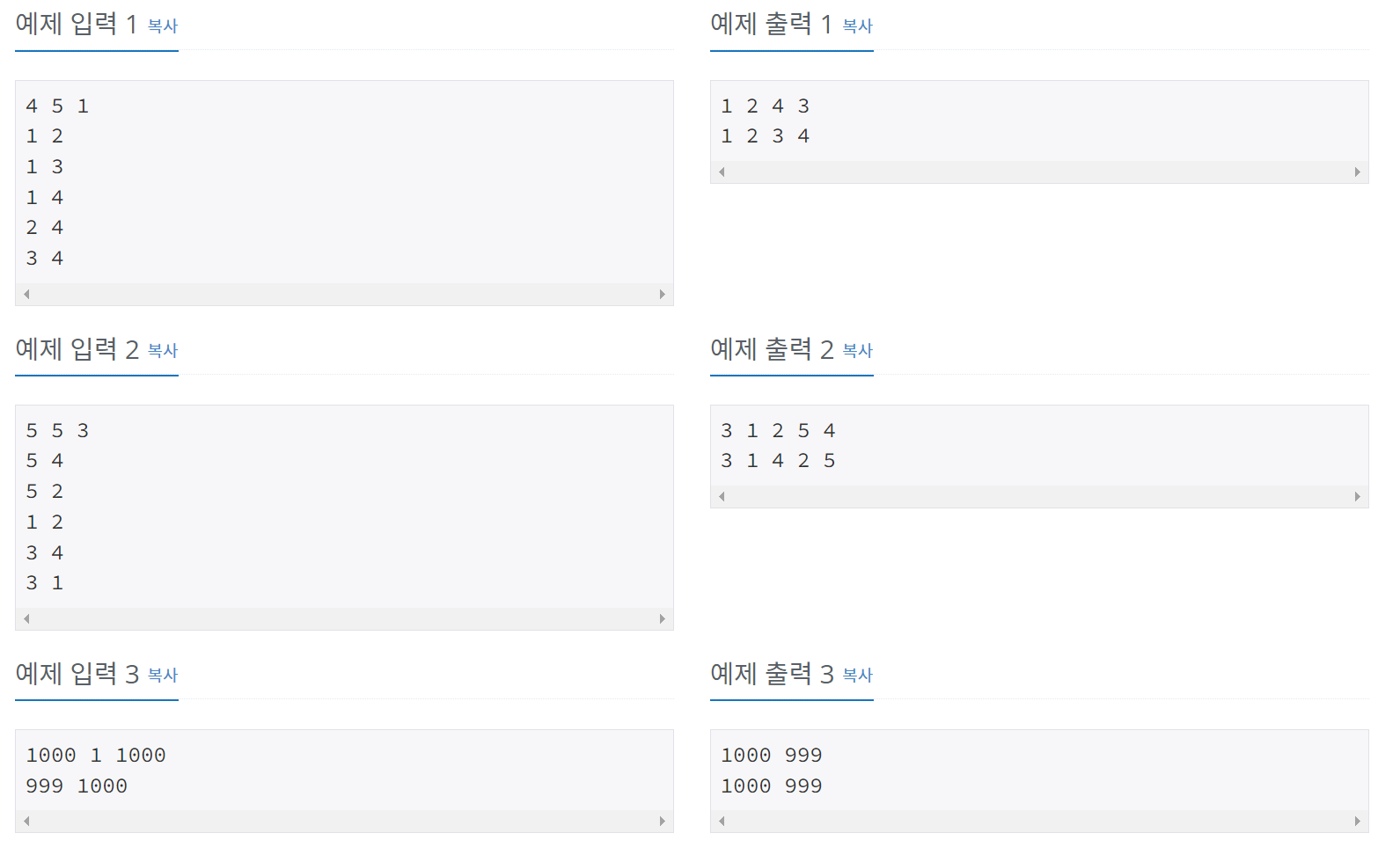
풀이
말 그대로 dfs와 bfs를 구현하면 된다. 각각의 함수에서 dfs는 함수를 호출했을 때 입력된 인자를, bfs는 while문의 루프가 돌아갈 때 입력된 인자를 출력하는 것이 문제에서 구하고자 하는 수행 순서이다. 방문할 수 있는 정점이 여러개인 경우에는 정점 번호가 작은 것을 먼저 방문하라 하였으므로, 그래프를 오름차순으로 정렬한 후에 dfs와 bfs를 실행하면 된다.
소스 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class dfs와bfs {
static boolean[] visited;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] arr;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
arr = new ArrayList[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i < n+1; i++) {
arr[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
arr[a].add(b);
arr[b].add(a);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n+1; i++) {
Collections.sort(arr[i]);
}
visited = new boolean[n+1];
dfs(v);
System.out.println();
visited = new boolean[n+1];
bfs(v);
}
static void dfs(int v) {
if (visited[v])
return;
System.out.print(v + " ");
visited[v] = true;
for (int i : arr[v]) {
if(!visited[i]) {
dfs(i);
}
}
}
static void bfs(int v) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(v);
visited[v] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int now = q.poll();
System.out.print(now + " ");
for (int i : arr[now]) {
if (!visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
q.add(i);
}
}
}
}
}
태클 감사합니다.
조언 환영입니다.
